What Is Dementia Dsm V
Dementia is commonly associated with more than 1 neuropathology usually Alzheimer disease with cerebrovascular pathology. A pivotal addition is.
Ppt Preview Of The Dsm 5 For School Psychologists Powerpoint Presentation Id 1086749
Dementia was named major neurocognitive disorder NCD in the DSM-5.

What is dementia dsm v. The new terms focus on a decline rather than a deficit in function. It is distinct from mental illness. The DSM-5 distinguishes between mild and major neurocognitive disorders.
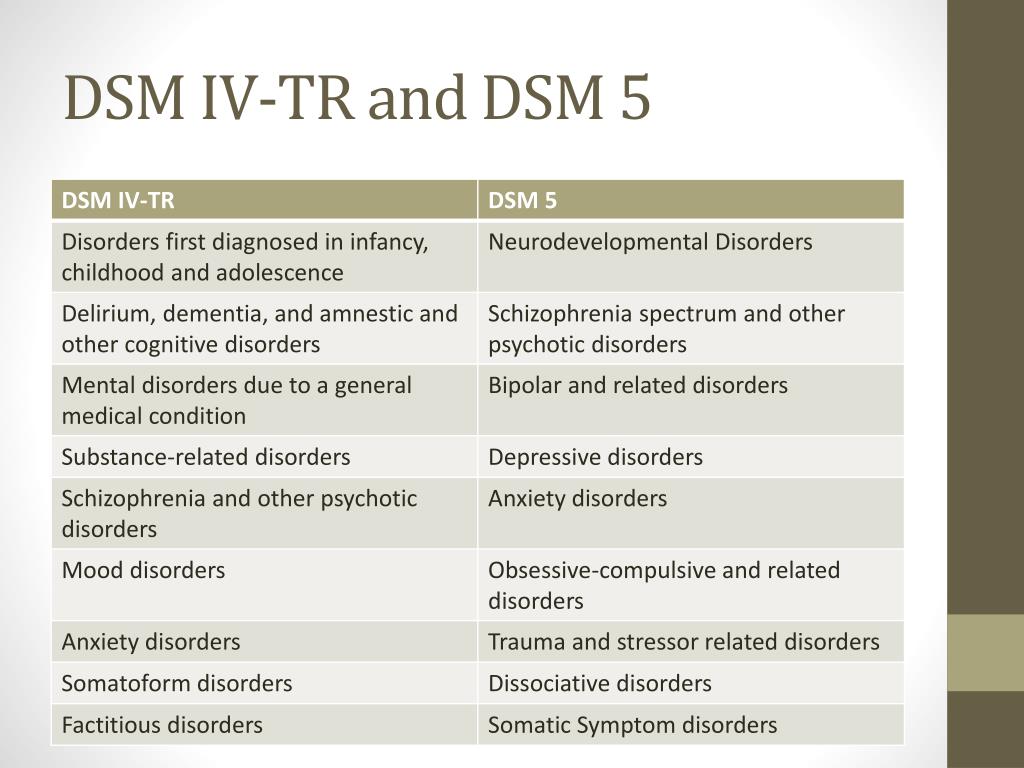
Dementia DSM-IV-TR 2904029044 29410 29411 2948 Dementia is a syndrome of multiple different etiologies characterized by a global decrement in cognitive functioning occurring in a clear sensorium. In the DSM-5 the term dementia is replaced with major neurocognitive disorder and mild neurocognitive disorder. Major neurocognitive disorder replaces the DSM-IVs term dementia or other debilitating conditions.
Perhaps the most dramatic change related to these conditions in the draft DSM-V is the proposal to drop the term Dementia and replace it with the term Major Neurocognitive Disorder The stated rationale for the proposed change mostly focuses on nosological considerations that seem on the whole sensible to address. Major neurocognitive disorder known previously as dementia is a decline in mental ability severe enough to interfere with independence and daily life. Diagnosing dementia requires a history.
Show full abstract DSM-III criteria for primary degenerative dementia and had a score of 5 points or more on the GNAS and a score of 6 points or less on the HIS. This change to neurocognitive disorder NCD is an effort to distance the condition from any stigma attached to the word dementia. Neurocognitive Disorder Dementia is the umbrella term for a number of neurological conditions of which the major symptom is the decline in brain function due to physical changes in the brain.
In the United States Alzheimer disease one cause of dementia affects 58 million people. The DSM-5 also recognises a less severe level of cognitive impairment mild. New diagnostic criteria for dementia were developed and released in 2013.
However the term dementia may still be used as an acceptable alternative. Mixed dementia is a condition in which brain changes of more than one type of dementia occur simultaneously. Picks disease is a degenerative disease of the brain that particularly affects the frontal.
The second noticeable change is that the dementia chapter in DSM-5 is titled Neurocognitive Disorders whereas in DSM-IV it was titled Delirium Dementia Amnestic and Other Cognitive Disorders. But interestingly the rationale also notes that the term dementia has. The word dementia is derived from a Latin word meaning mad or insane.
Though not confused patients have difficulty with short-term memory and to a relatively lesser degree long-term memory. The first and most obvious change in the newest version is that the Roman numeral V has been replaced with the Arabic numeral 5. DSM-IV criteria for dementia.
The presence of Dementia Due to Other General Medical Condition eg Picks disease. The essential feature of Dementia Due to Picks Disease is the presence of a dementia that is judged to be the direct pathophysiological consequence of Picks disease. The term in DSM IV was Delirium Dementia and Amnestic and Other Cognitive Disorders which the committee felt was unwieldy and did not represent a conceptual whole.
- Learning and memory. Many different types of dementia exist and many conditions cause it. The Diagnostic and Statistic Manual of Mental Disorders Fifth Edition DSM-5 classifies neurocognitive disorders NCDs or dementia as mild or major depending on how severe they are.
Dementia describes a group of symptoms associated with a decline in memory reasoning or other thinking skills. The total GBS score the GBS. Evidence of significant cognitive decline from a previous level of performance in one or more cognitive domains.
Dementia is an acquired loss of cognition in multiple cognitive domains sufficiently severe to affect social or occupational function. In DSM-IV this disorder is called Dementia Due to Picks Disease. This term was introduced when the American Psychiatric Association APA released the fifth edition of its Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders DSM-5.
The new term is simpler and encompasses a range of disorders in which the primaryprincipal manifestation is an acquired loss of. The DSM-5 replaces the term dementia with major neurocognitive disorder and mild neurocognitive disorder. Memory impairment Aphasia Apraxia Agnosia Executive dysfunction.
The Diagnostic Statistical Manual-5 DSM-5 has included a category named the neurocognitive disorder which was formally known in DSM-IV as dementia delirium amnestic and other cognitive disorders. Major NCD is equivalent to dementia. The clinical course of Vascular Dementia is variable and typically progresses in stepwise fashion.
In Vascular Dementia focal neurological signs eg exaggeration of deep tendon reflexes extensor plantar response and laboratory evidence of vascular disease judged to be related to the dementia are present. DSM-5 criteria for major neurocognitive disorder. For more information see Dementia Due to Other General Medical Conditions.
The two terms are essentially different labels for the same condition. Changes in DSM 5 from DSM IV. The term dementia is still used but usually to refer to degenerative.
Complex attention Executive function Learning memory Language Perceptual-motor Social cognition DSM-IV.

No Financial Disclosures We Will Be Discussing Off Label Use Of Psychotropic Medications To Treat Dementia Ppt Download

Evaluation Of Dsm 5 And Iwg 2 Criteria For The Diagnosis Of Alzheimer S Disease And Dementia With Lewy Bodies Semantic Scholar

Dsm 5 In Vascular Dementia Comparison With Other Diagnostic Criteria In A Retrospective Study Semantic Scholar

Objectives N Differentiate Delirium From Dementia N Differentiate

Clinical Features In Delirium Not Currently Defined By Dsm Criteria Download Table
Classifying Neurocognitive Disorders The Dsm 5 Approach Nature Reviews Neurology

Dementia What S New In Medicine 2014 September 13 Ppt Download

Vascular Dementia Chapter 30 The Behavioral And Cognitive Neurology Of Stroke

Delirium The Diagnostic And Statistical Manual Of Mental Disorders Fifth Edition Dsm 5 Diagnostic Criteria For Delirium Is As Follows Disturbance Ppt Download
Https Ndafp Org Image Cache Dementia In The Office Pdf
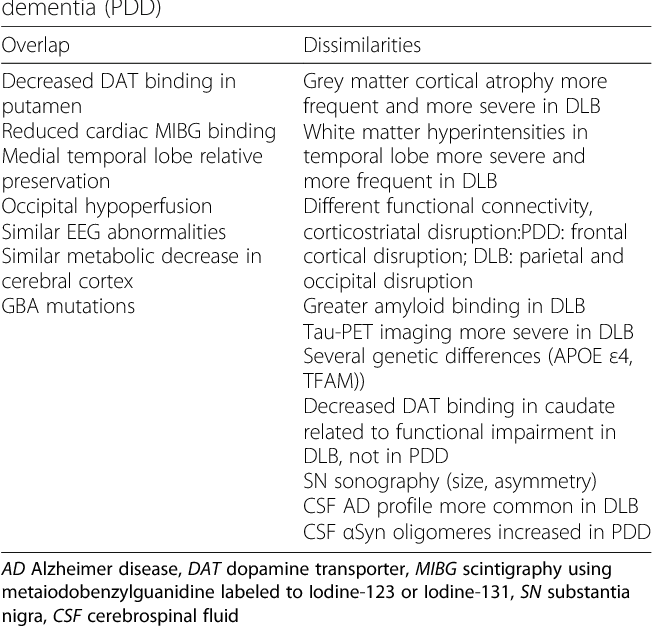
Table 2 From Are Dementia With Lewy Bodies And Parkinson S Disease Dementia The Same Disease Semantic Scholar

Application Of The Dsm 5 Criteria For Major Neurocognitive Disorder To Vascular Mci Patients Semantic Scholar
Https Www Ndafp Org Image Cache Dementia In The Officehandout Pdf

Dementia Neurocognitive Disorders Ppt Download

Pdf Diagnostic And Statistical Manual 5 And Dementia Fine Print Finer Points

Alzheimer S Disease Interventions And New Findings Ppt Download

Dsm 5 New Concept Of Major Neurocognitive Disorder In Dsm 5 Ppt Video Online Download

Neurocognitive Domains Classifying Neurocognitive Disorders The Dsm 5 Approach Nature Reviews Neurology Dsm 5 Cognitive Domain Dsm

Post a Comment for "What Is Dementia Dsm V"